TURNER SYNDROME
What is the other name of Turner Syndrome?
Ullrich-Turner syndrome
What is the m/c sex chromosome disorder in female?
Turner syndrome and occurs in approximately 1 in 2000 to 1 in 2500 live female births.
What are the genotypes of Turner syndrome?
45X monosomy in 45% of cases
45X mosaicism with normal cell line in 15% cases
X chromosome anomalies like - Isochromosome, Ring chromosome, Xp or Xq deletion
Y chromosome mosaicism in 10-12% cases.
What gene is responsible for short stature in Turner syndrome?
SHOX (short stature homeobox-containing gene on the X-chromosome) is associated with short stature in Turner syndrome and in Leri-Weill dyschondrosteosis.
What gene is responsible for gonadal insufficiency in Turner syndrome?
BMP15 (bone morphogenetic protein 15 (BMP15) on the short arm of the X chromosome (Xp)).
What is the frequency of the 45X karyotype at conception?
3% approx, but 99% of these are spontaneously aborted, accounting for 5–10% of all abortuses.
Mosaics are found to be less common in aborted fetuses suggesting preferential survival of mosaics.
What is the most characteristic c/f o turner syndrome?
Short stature.
What are other clinical features characteristic of TS?
Webbing of neck
Low posterior hair line
Small mandible
Prominent ears
Epicanthal folds
high arched palate
Shield chest - a broad chest presenting the illusion of wide spaced nipple
cubitus valgus
Hyperconvex finger nails
What are the recognizable findings at birth in a case of turner syndrome?
Edema of the dorsa of the hands and feet and loose skinfolds at the nape of the neck. Low birthweight and decreased birth length are common
What is the stature like in TS?
Short and stocky appearance.
For height monitoring growth charts are specifically available for TS patient.
Stocky appearance is d/t relatively greater reduction in body height than width and because many girls are overweight.
The growth failure is further compounded by delayed puberty, with lack of a growth spurt.
Adult height is correlated with parental stature, as it is in the general population, but the height is significantly less than would be predicted for a girl without Turner syndrome.
What are other skeletal abnormalities associated with TS?
Scoliosis
Madelung deformity
Cubitus valgus(increased carrying angle of elbow;present in 50% of cases)
Genu valgum
Genu varum
Short fourth metacarpal and or metatarsal.
Sternal malformations
congenital hip dysplasia
What is Madelung deformity?
Bayonet deformity of the wrist
Prominent ulnar head and apparent volar subluxation of the wrist on the forearm d/t shortening of the radius and relative overgrowth of the ulna. It is seen in case of TS.
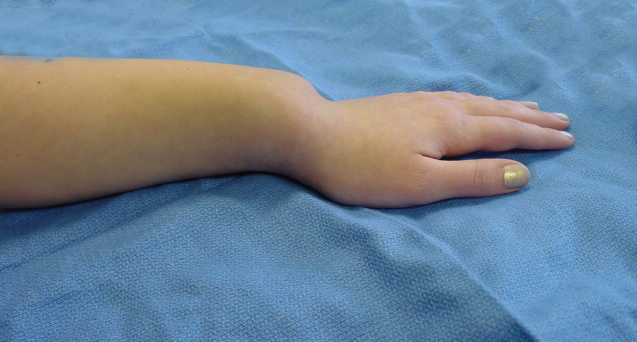
Why ovarian failure occurs in TS female?
The normal fetal ovary contains approximately 7 million oocytes, but these begin to disappear rapidly after the 5th mo of gestation. At birth, there are only 2 million (1 million active follicles); by menarche, there are 400,000-500,000; and at menopause, 10,000 remain. In the absence of 1 X chromosome, this process is accelerated, and nearly all oocytes are gone by 2 yr of age.
Eventually, the ovaries are described as streaks and consist only of connective tissue, with very few germ cells present.
Primary hypogonadism is one of the most common features of Turner syndrome, and TS is one of the most common causes of premature ovarian failure.
What about the sexual maturation in TS patient?
Sexual maturation (breast development) fails to occur at the expected age; however, signs of adrenarche (pubic hair) are normally present.
What is the risk of CVS disease in TS?
There is a 4-5–fold increase in the rate of premature mortality secondary to congenital heart disease and premature coronary heart disease in adults with Turner syndrome.
What are the common CVS anomalies associated with TS?
Aortic valve defects (primarily bicuspid aortic valves) - 1/3rd cases
Elongated transverse aortic arch
Coarctation - 20% cases
What are the risk factors for heart disease?
Webbing of neck
45X haploinsufficiency
Increased thoracic anterior-to-posterior diameters
Renal anomalies
hypertension.
Hypertension and vasculopathy are more common in TS female in comparision to healthy control.
What are the renal anomalies associated with TS?
30-40 % cases have renal malformations.
The more common abnormalities include collecting system malformations (20 percent) and positional abnormalities, as well as horseshoe kidneys (10 percent). The latter anomaly is more often observed in patients with the 45,X karyotype.
Pelvic kidney.
PUJ obstruction.
Horse shoe shaped
Double collecting system.
Absence of 1 kidney
What are metabolic and endocrine associations of TS?
Antithyroid antibodies (thyroid peroxidase and/or thyroglobulin antibodies) occur in 30–50% of patients.
Autoimmune thyroid disease, with or without the presence of a goiter, occurs in 10–30% of patients.
Abnormal glucose tolerance and insulin resistance and, only rarely, frank type 2 diabetes occur in older patients with Turner syndrome.
Impaired insulin secretion has been described in 45,X women.
Cholesterol levels are elevated in adolescence, regardless of body mass index or karyotype.
Risk of osteoporosis is increased.
What are GI malformations associated with TS?
UC, crohns dz, Celiac ds
What are dermatological changes?
Pigmented nevi
Melanocytic nevi
Essential hyperhidrosis
Alopecia areata
Torus mandibularis
What are the ear findings?
Bilateral recurrent otitis media present in 75% cases.
Increased risk cholesteatoma.
SNHL is common with frequency increasing with age
What about IQ?
Normal except in TS d/t ring chromosome.
In adults, deficits in perceptual spatial skills are more common than they are in the general population.
What is the risk of malignancy in TS?
Mosaicism involving the Y chromosome is associated with gonadoblastoma in 7-10% cases.
Therefore the recommendation is that prophylactic gonadectomy should be performed even in the absence of MRI or CT evidence of tumors. The recommended timing of this
procedure is at the time of diagnosis, but this may need to be reevaluated in the
future.
How do we proceed with diagnosis in suspected cases?
Chromosomal analysis -karyotyping
USG of kidney,ovaries and heart
What about the FSH levels?
It is markedly elevated to greater than those of age-matched controls during infancy; at 2-3 yr of age, a progressive decrease in levels occurs until they reach a nadir at 6-8 yr of age, and by 10-11 yr of age, they rise to adult castrate levels.
What other lab tests should be done?
Screen for thyroid antibodies
Screen for celiac disease
LFT - elevated
How do we treat TS?
Human recombinant GH replacement and sometimes in association with anabolic steroid OxandroloneEstrogen for sexual maturation -- early estrogen therapy at around 12-13 years
Estrogen therapyimproves verbal and nonverbal memory in females with Turner syndrome.
Is pregnancy possible in female with TS?
Yes by IVF or ovum donation.


Comments
Post a Comment