Spinal muscular atrophy
What type of disease is SMN?
It is a degenerative disorder of spinal motor neuron.
What causes SMN?
Homozygous mutation of SMN1 gene on exon 7 of
chromosome 7
AR and X linked are also present but rare
What is the most common casue of infant mortality among AR disorders?
Spinal Muscular atrophy
Which is the most prevalent AR disorder at birth?
Cystic Fibrosis f/b SMA
What is the function of SMN1?
SMN protein appears to play a role in mRNA synthesis in motor
neurons and also may inhibit apoptosis.
What determines the activity of SMN1 gene & phenotypic expression of SMA?
Modifying gene called SMN2
Loss of the SMN1 protein is partially compensated by SMN2 protein synthesis, a mechanism that explains some but not all of the phenotypic variability in patients with SMA.
Disease severity in SMA generally correlates inversely with SMN2 copy number, which varies from 0 to 8 in the normal population, and to a lesser degree with the level of SMN protein.
The presence of >3 copies of SMN2 is associated with a milder phenotype
What are the types of SMA?
SMA0
SMA1
SMA2
SMA3
SMA4
Which cranial nerves and spinal nerves are spared?
Motor neurons of cranial nerves III, IV, and
VI to the extraocular muscles, as well as those of the sacral spinal cord
innervating striated muscle of the urethral and anal sphincters, are
selectively spared.
The upper motor neurons (layer 5 pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex) also remain normal.
What is the pathological hallmark of SMA?
The pathologic hallmark of SMA is the progressive
denervation of muscle.
This is compensated for in part by reinnervation from an adjacent motor unit,
but giant motor units are thus created, with subsequent atrophy of muscle
fibers when the reinnervating motor neuron eventually becomes involved.
What
part of NS is affected in SMA?
Anterior horn cells is Spinal cord &
motor nuclei in the lower brainstem
Cognition is unaffected.
On what basis the SMA are classified?
On the basis of age of onset, milestones achied and clinical
course.
What is the most common type of SMA?
Type 1
Which is most severe form of SMA?
Type 1 and type 0
What is the function of SMN1 that is defective in SMA?
The SMN
gene is responsible for stopping the programmed cell deathof neuroblasts and
other neurons formed from neuroectoderm and lack of this function leads to
iuninhibited death of motor neurons.
Which is most severe form of SMA?
SMA type 0 and type 1
Which is the least severe type of SMA?
Type 4 – adult onset type
What is the classical clinical feature of SMA?
Diffuse, symmetrical proximal muscle weakness which is
greater in the lower limbs than the upper limbs with absent or markedly reduced
tendon reflexes.
Frog leg position

Tongue fasciculations
Selective involvement of axial and intercostal muscles but
sparing of diaphragm because of which they have a characteristic paradoxical
abdominal breathing pattern
Inverted V shaped upper lip.
Bell shaped chest
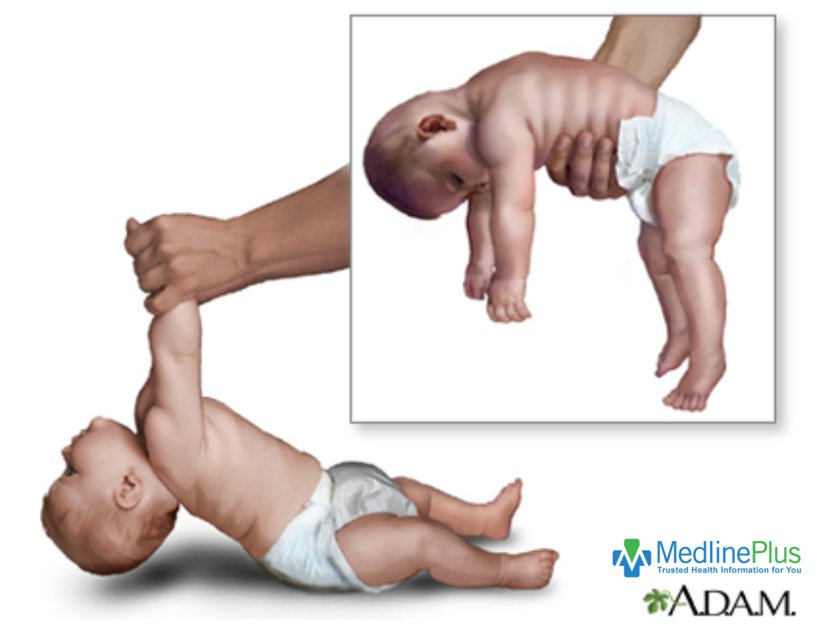

What about the respiratory insufficiency in SMA cases?
SMA is
associated with a restrictive, progressive respiratory insufficiency,
particularly SMA type 0 and type 1
What other congenital anomalies are a/w SMA?
Sleep disturbances
Congenital
heart defects may be present with SMA type 0
While
there have been occasional reports of heart rhythm abnormalities in SMA types
1, 2, and 3, these may be coincidental associations.
What is the prenatal form of SMA?
SMA type 0
where degeneration of motor neurons begin in midgestation period.
What are the features of SMA type 0?
Most severe
form
Death by 6
months and usually by 1 month
Death occurs
d/t respiratory insufficiency
What can be the maternal complains in case of SMA type 0?
Mother may
recognize the decrease fetal movements.
What are the clinical features of SMA type 0?
Hypotonia
Severe weakness
Areflexia
Facial
diplegia
CHD
Arthrogyropsis
(multiple joint contractures
No milestones
achieved
What is fetal hypokinesia deformation sequence?
Infants with SMA of neonatal onset may present with signs of
fetal hypokinesia deformation sequence, including polyhydramnios, intrauterine
growth retardation, skeletal abnormalities with multiple articular
contractures, and pulmonary hypoplasia.
How many copies of SMN2 do SMA0 have?
Only one copy
What are the types of SMA1?
SMA1a - severe weakness
from birth or the neonatal period; head
control is never
achieved.
SMA
1b - presentation after the neonatal period, within the
first 2 mo; head
control is never achieved.
SMA
1c - onset after the neonatal period but head control is achieved, and some of
the infants may gain the ability to sit with support.
What are the features of SMA 1?
All
the features of SMA described as above.
Respiratory
failure, sucking & swallowing difficulties depends on type of SMA 1.
What is the other name for SMA1?
Werdnig
Hoffmann Disease
What
is the prognosis of SMA 1?
SMA
1a die within 6 months of age
SMA
1b & 1c die within 2 years if no respiratory support is provided
What is the facial feature like in SMA 1?
SMA
type I have an alert and bright expression with preserved cognitive
functions. There
is no involvement of the facial and extraocular muscles at presentation,
although facial weakness does occur at later stages of the disease.
However,
due to the involvement of bulbar there is difficulty is sucking, swallowing and
there is pooling of secretion
How many copies of SMN2 is present in SMA1?
2
or 3 copies
What anomalies are a/w SMA?
Early-stage
developmental congenital heart defects described in severe SMA patients,
generally carrying one copy of SMN2, include atrial
septal defects, a dilated right ventricle,ventricular septal defects, and
hypoplastic left heart syndrome.
Autonomic
nervous system, which may result in arrhythmia and sudden death.
Vasculopathy
can be another rare presentation, and ulceration and necrosis of the fingers
and toes have also been described in two severe type I SMA patients
What is the type 2 SMA?
Intermediate
form of SMA
Aka
Dubowitz disease
Onset of
6-18 months
How common is SMA type 2?
30% of
cases
What is the prognosis of SMA 2?
>2 years
and about 70 % survive to 25 years of age
What milestones are achieved in SMA 2?
Able to
sit without support but never stands or walks
What are other features of SMA 2?
Scoliosis –
d/t progressive muscle weakness
Late onset
respiratory muscle weakness – leading to restrictive lung disease
Average or
above average muscle weakness
A fine
tremor like form of myoclonus aka minipolymyoclonus affecting distal limbs
How many copies of SMN2 are present in SMA 2?
3 copies
in 80 % cases
What is type 3 SMA?
Juvenile
form
Kugelberg-Welander
disease
How common is SMA 3?
10% cases
Walker SMAs
When is
the age of onset of SMA 3?
>18
MONTHS < 3 YEARS FOR 3A AND > 3 YEARS FOR 3B
Which muscle is particularly involved in type 3?
Shoulder girdle
muscles
What
milestones are achieved in SMA 3?
They are
almost normal
Bulbar involvement
Is rare
Respiratory
involvement is rare
How about the muscles in SMA 3?
Instead of
atrophy hypertrophy and often confused with muscular dystrophies
What about the prognosis of SMA3?
Most cases
gradually develop inability to walk and become wheel chair bound
Almost
normal life span
What about fasciculations in SMA 3?
Present
Best to
observe in tongue
Can be
present in biceps brachii and deltoid
Polyminimyoclonus
may be present
What about type 4 SMA?
Onset in 2nd
or 3rd decade of life
Mild
weakness
Normal IQ
Often they
have better IQ
What is the prognosis of Type 4 SMA?
Normal life
span
But progressive
deterioration of ambulation and the high risk of falling and fracturing long
bones or the pelvis eventually require use of a wheelchair; an electric
wheelchair often is needed because weakness of the upper extremities does not
allow the patient to manually push the wheels.
Progressive
scoliosis is another serious complication.
How do we diagnose SMA case?
Creatine
kinase level may be normal but commonly mildly elevated (2-4 fold) but usually
not more than 10 fold
CXR
– thin ribs
What is the use of ECG in SMA cases?
Electrocardiography
(EKG) may serve as a simple and practical tool in patients with SMA to
demonstrate a baseline tremor as an artefact representing muscle fibrillations
more prominent on lead II.
Finding
of Nerve conduction studies in SMN
Normal
except for mild slowing in terminal stages of the disease and helps in
distinguishing SMA from peripheral neuropathy.
What is electromyography finding in SMA?
EMG
shows fibrillation potentials and other signs of the denervation of muscle.
There is no need for a muscle biopsy, which demonstrates a neurogenic pattern
with group atrophy in all forms of SMA.
How do we diagnose SMA?
Molecular
genetic testing with targeted mutational analysis can confirm the diagnosis and
SMN2 copy number testing.
Absence
of SMN1 exon 7 confirms diagnosis
Real
time PCR and Multiplex-ligation dependent probe amplification (MLPA) gives a
quick and reliable results.
What is the sensitivity and specificity of genetic testing and how can we further improve?
95%
sensitivity and 100 % specificity
Semiquantitative
assays improve the diagnostic sensitivity up to 98%.
What type of mutations are most often identified in SMA based on molecular testing?
What is the difference between SMN1 and SMN2 gene?
The
critical difference between SMN1 and SMN2 is a cytosine (C)
to thymine (T) transition in exon 7 of SMN2
Both SMN1 and SMN2 genes can produce the full-length SMN mRNA transcript
required to make normal SMN protein, along with other more unstable transcripts.
However, while the full-length transcript is the major product of SMN1, SMN2 produces
smaller amounts of the full-length SMN mRNA transcript and hence smaller
amounts of full-length (functional) SMN protein.
Where are SMN protein encoded by SMN gene located?
It is localized in a bright dot like structure called gems
(gemini of Cajal bodies) in the nucleus
What are the pathophysiological findings in case of SMA?
What determines the severity of disease?
As
mentioned earlier SMN2 copy number – major protective modifier
Amount
of functional SMN1 protein
Genetic
modifiers like plastin 3 and neurocalcin.
Can we diagnose SMA prenatally?
Yes
by CVS and amniocentesis
Newborn
screening in SMA cases
Pre-symptomatic
SMA can be diagnosed by NBS
DNA
extracted from newborn blood spots is tested using real-time PCR.
Challenges
in newborn screening include the inability to detect carriers of heterozygous
deletions of SMN1, and SMN2 copy numbers.
How do we manage cases of SMA?
Management
of complications –
Respiratory
ailments
Nutritional
Orthopedic
physiotherapy
Other
organ involvement
Psychological
Specific
agents for treatment
What are the specific agents for treatment of SMA?
Nusinersen
– anti-sense oligonucleotide that modifies splicing of the SMN2 gene to
increase production of normal, full-length survival motor neuron protein, which
is deficient in SMA.
What is the dosing of nusinersen?
5ml
= 12 mg given intrathecally
Treatment
is initiated with four loading doses; the first three loading doses are given
at 14-day intervals, while the fourth loading dose is given 30 days after the
third. Thereafter, a maintenance dose is given once every four months. The cost
of each dose is listed as $125,000.
Which TRIALS led to the approval of nusinersen for treatment of SMA?
ENDEAR
trial for < 6months old children
CHERISH
trial for 2 to 12 years
After FDA
approval, children enrolled in ENDEAR, CHERISH, and other nusinersen trials
were eligible to participate in a phase 3 extension study named SHINE
US
FDA and European medicines Agency has approved nusinersen for use.
What is the role of gene therapy in SMA patients?
Onasemnogene
abeparvovec is a recombinant adeno-associated viral vector containing complementary
DNA encoding for the normal SMN1 protein.
Approved
for FDA for use in children < 2 yrs of age.
What is the dosing of gene therapy?
Single
dose
Steroids
started 1 day before the therapy
Montor
for AST and ALT
What is the cost of Onasemnogene abeparvovec?
2,125,000
$
What is the role of oral olesoxime?
Phase 2 studies with oral olesoxime (TRO19622) in the SMA type II or nonambulant type III patient population showed stabilization or improvement compared with placebo.
Although the primary endpoint was not met, olesoxime was safe and might be used in combination with other drugs targeting other mechanisms of the disease.
What are the non-5q SMAs?
Inherited
SMAs which are not caused due to SMN mutation/deletion in chromosome 5. Although very rare, non-5q SMA forms are clinically
and genetically heterogeneous.
SMA
Jokela type
Fazio-Londe
disease, bulbar palsy

Comments
Post a Comment